At Being Guided we help organisations to adopt Artificial Intelligence (AI) in a safe and measured way. This means embracing AI to not only automate but also augment human tasks and reduce IT and operational costs.
However, although you may have worked with the publicly available AI products, such as Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, ChatGPT-4o mini or xAI Grok, for enterprise class Digital Transformations we often see AI as being viewed as 'a solution in search of a problem'. The noise surrounding AI is understandably bewildering. Clarity and a detailed explanation is called for!
So, this blog post is my attempt to give the enterprise a way forward that generates meaningful outcomes from AI-Enabled Digital Transformation in the enterprise. At Being Guided it starts with our three Design Principles, as outlined below.

Three Design Principles
Our Design Principles for AI-Enabled Digital Transformation in the enterprise are:
1. Meaningful Journey
AI can either augment or automate human tasks. In both use case scenarios it is important to make the journey through one or more tasks as intuitive and meaningful as possible. This is especially true where AI acts as a copilot to accelerate and reduce errors in knowledge-intensive tasks.
2. Fierce Reduction
AI has a crucial role to play in simplifying processes and related information technology. This simply means eliminating everything you can when AI Enabling existing IT systems. Reducing time-to-decision in document-intensive industries is often a powerful initial use case for AI Enabling.
3. Progressive Disclosure
For augmenting or automating tasks with AI it is better to take more steps with fewer instructions per step. With a 'human-in-the-loop' this avoids cognitive overload per screen. This is where our AI Discovery approach generates an optimised AI Enabling measurable value outcome.

Introducing Supercog
Supercog are our AI Venture Partners: a US-based startup creating a powerful AI Agent Platform, as described further on in this blog post.
Our expertise is oriented towards delivering Supercog AI Agent Platform with Salesforce and the many applications that are integrated with this market-leading technology. Our early adopters with Supercog AI-Powered Digital Innovation include NHS and Arts Care.
In our recent NHS work we have applied Supercog to enable the reduction of development time for integrating Salesforce with mission-critical Electronic Health Records (via HL7 messaging) and Patient Appointments. Here, Supercog, acting as copilot, reduced development hours by 70%+.
As Open Source is an important part of the enterprise IT mix, we have also extensive know-how with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and JavaScript backend and frontend systems. A recent example for us was creating a Proxy Server middleware layer for NHS Salesforce integration.
Our scope is broadening to include other familiar technologies: Amazon S3, Discord, DuckDB, Google Workplace, Hubspot, Jira, Microsoft Dynamics, Microsoft Office 365, ServiceNow, Slack, Snowflake, YouTube and Zapier. Over time, this list will grow.
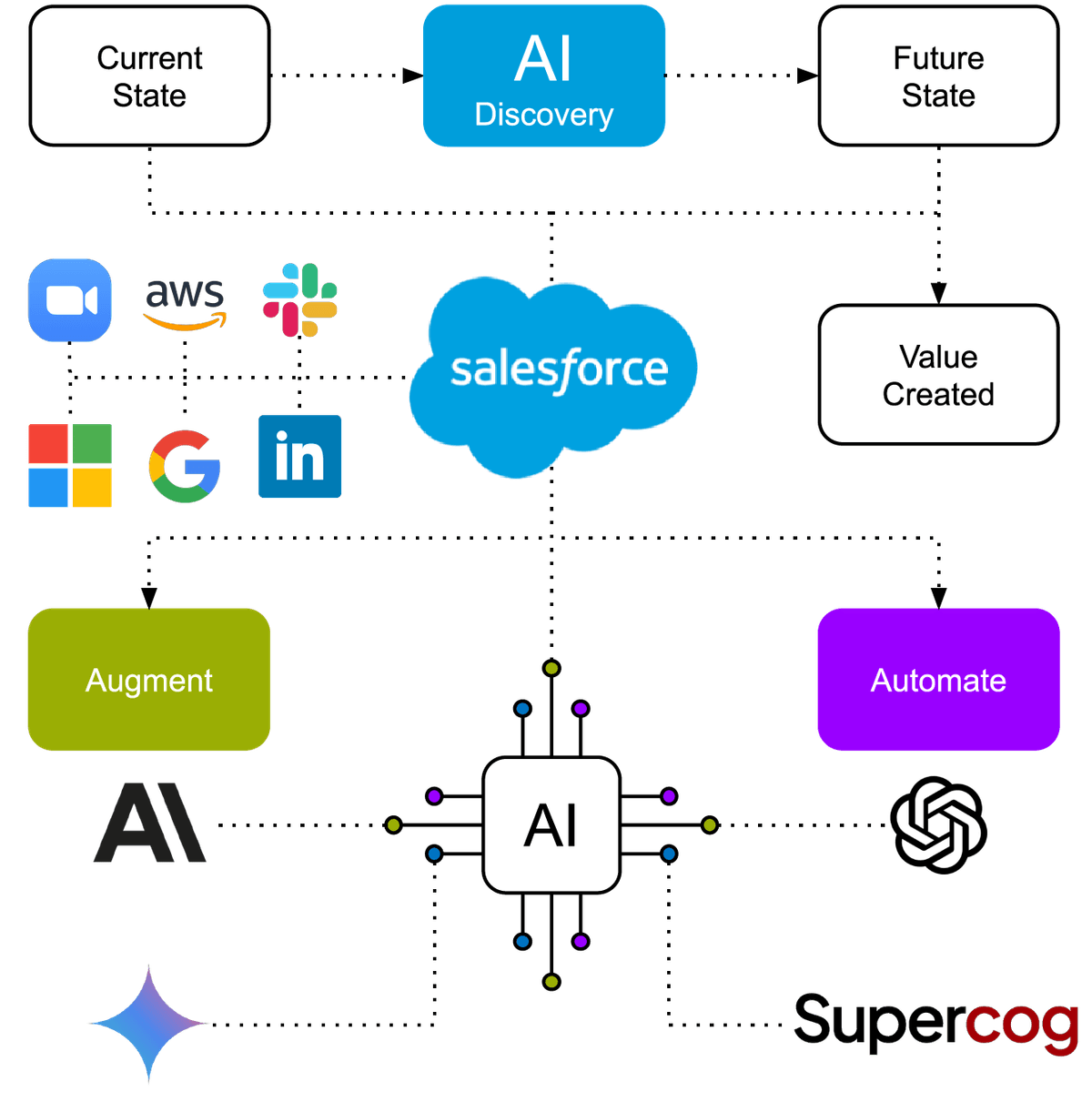
AI Discovery
In our engagements at Being Guided, we apply Design Thinking and Value Engineering tools. This helps our customers and partners determine '5W1H': the Why, Where, What, Who, Where and How AI can deliver measurable advantages.
As shown in the infographic above, this is dividing AI Discovery into three categories:
- Augmentation of human tasks.
- Automation of human tasks
- No change of human tasks (yet).
It is highly likely that in your business (or your client's business), AI-Powered Digital Transformation will be a combination of all three categories. This is where 1 moves into 2, and, over time, 3 moves into 1. or 2.
From the AI Discovery a solid business case for AI Enabling must be generated.
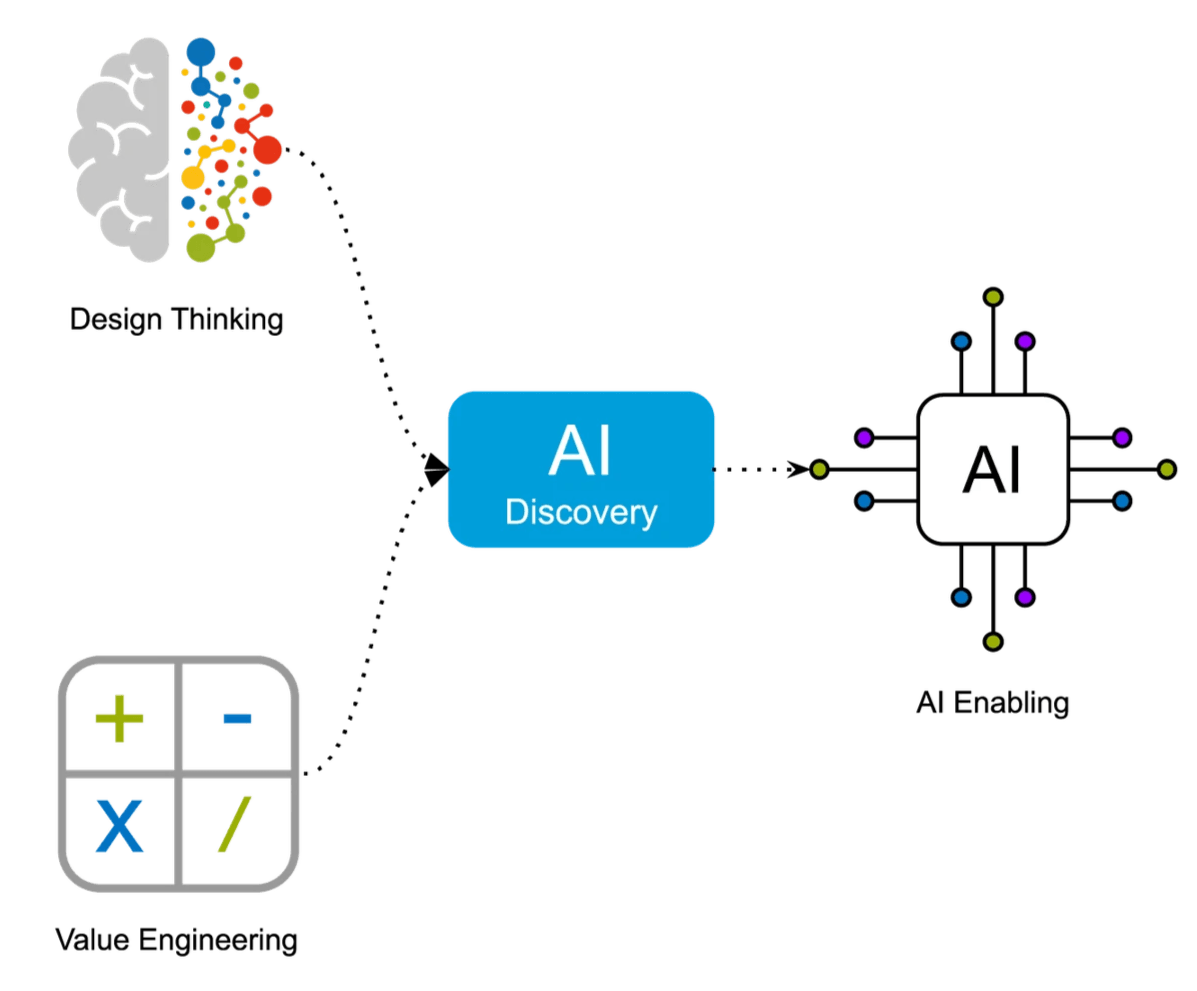
Design Thinking
Design Thinking means, as the name implies: thinking (and acting) like a designer. Being curious, restless and constantly challenging business-as-usual. It is all about solving problems in a people-oriented way. Being human-first to enable AI-first outcomes.
Design Thinking is our technology enabler for AI-Powered Digital Innovation. This is inspired by Hasso Plattner Institute of Design and Stanford University d.school1. At Being Guided we combine Design Thinking and Value Engineering as the two elements of an AI Discovery engagement.
We follow the work of Michael Lewrick and Omar Hatamleh2, the authors of AI and Innovation, where key topics covered are: core concepts of AI; generating a roadmap of change; transforming the ways of working; and, preparing for the future of AI.
We are further inspired by Jeanne Liedtka, Elizabeth Chen, Natalie Foley and Devis Kester3, the authors of The Experiementation Field Book. This is key to our work and to quote this book:
"Experimentation protects you from overspending on a solution that will not work for the people you designed it for. By placing small bets and learning at a fast pace, you can learn whether your concept really fulfills the unmet needs of your users."
The Stanford d.school Design Thinking method provides six (6) stages: Empathize; Define; Ideate; Prototype; Test; and, Implement. This offers a structured yet flexible framework to better understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems, and for us at Being Guided, rapidly co-create AI-Powered Digital Innovations with our customers and partners.
Stage 1. Empathize
Purpose: Understanding the users and their needs.
Application in AI-Powered Digital Innovation: In-depth user research, such as interviews, surveys, and observation, provides insights into user behaviours, needs, and motivations. This is crucial to ensure that the solution developed genuinely addresses real problems.
Stage 2. Define
Purpose: Clearly articulating the problem to be solved.
Application in AI-Powered Digital Innovation: After gathering user insights, define the core problem in a user-centered manner. This stage is about synthesising observations and articulating the problem in a way that guides the development of digital solutions.
Stage 3. Ideate
Purpose: Generating a range of creative ideas to solve the defined problem.
Application in AI-Powered Digital Innovation: This phase involves brainstorming and exploring a wide array of potential solutions, encouraging out-of-the-box thinking. It's essential for AI-Powered Digital Innovation, as it embraces creativity and leads to the discovery of effective digital solutions.
Stage 4. Prototype
Purpose: Turning ideas into tangible products.
Application in AI-Powered Digital Innovation: Prototyping involves developing scaled-down versions of the product or its specific features. Prototyping is crucial for visualising how digital solutions work and for gathering feedback before full-scale Implementation at stage 06: Implement.
Stage 5. Test
Purpose: Gathering feedback and refining the prototype.
Application in AI-Powered Digital Innovation: Testing includes formal test automation plus user trials and feedback collection on the solution. This helps in understanding the user experience, identifying issues, and validating the effectiveness of digitisation.
Stage 6. Implement
Purpose: Finalising the solution and launching it.
Application in AI-Powered Digital Innovation: The final stage involves finalising the design based on testing feedback, completing the development, and launching the solution. This phase ensures that the solution is polished, user-tested, and ready for everyday use.
Value Engineering
At Being Guided, as the name implies, we apply Value Engineering to determine value over price. This is calculating the cost of purchasing (or not purchasing) AI-Powered Digital Transformation in timely manner. This is quantifying time-based value versus the cost of remaining with IT business-as-usual.
Vale Engineering focuses on dividing AI Discovery into three categories:
1. Augmentation of human tasks.
2. Automation of human tasks.
3. No change of human tasks (yet).
For AI there will be a growing number of use cases where Usage Pricing, based on some form of metering of transactions or other measurable value is agreed. There may be use cases where it is blend of User Pricing and Usage Pricing works. Whatevever it is, it cannot be one size fits all.
For transaction-heavy automations, the cost of the underlying Large Language Model (LLM) driving the AI Enabling will be a key factor, but less so in light augmentation use cases.
We start with a simple question for the buyer:
What is the cost of NOT buying the AI-Powered Digital Transformation Solution?
Firstly, let's look at the Return On Investment (ROI) Model - a general formula:
ROI = (Cost of Investment / Net Profit)×100%
To adapt this formula for an As-Is vs. To-Be comparison, consider:
Net Profit: This will be the difference in profits between the Future State (To-Be) and the Current State (As-Is).
Cost of Investment: This is the cost incurred to move from the Current State (As-Is) to the Future State (To-Be).
Given the above considerations, the formula becomes:
ROI = (ProfitTo−Be − ProfitAs−Is / Cost of Transition) × 100%
Where:
Profit To-Be = Profit or (benefit) in Future State
Profit As-Is = Profit (or benefit) in Current State
Cost of Transition = Cost to move from As-Is to To-Be
Note: If you're measuring benefits other than strict monetary profits, such as time saved or other intangible benefits, ensure you can convert these benefits into a monetary value for this to be valid.
To calculate the Return On Investment (ROI) from AI-Powered Digital Innovation with the specified inputs, we can formulate several equations. Let's define the variables first:
BVAs-Is = Current State (As-Is) Business Value generated per annum without Solution.
BVTo-Be = Future State (To-Be) Business Value generated per annum after investing in Solution.
COS = Cost of Solution.
ROI = Return on Investment as a ratio relative to the Cost of Solution.
CoD = Cost of Delay per day when not investing in Solution.
CoDN = Cost of Doing Nothing per day when not investing in Solution.
CoDday = Cost of Delay per day when not investing in Solution.
CoDNday = Cost of Doing Nothing per day when not investing in Solution.
Calculating ROI from Solution:
Net_Gain - BVTo-Be - BVAs-Is
Calculating ROI:
ROI - Net_Gain - CDI / CDI
The ROI is expressed as a ratio. Multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
Cost of Delay (CoD):
This represents the loss per day by delaying the Solution purchase. Assume the delay starts from the beginning of the year and goes on for d days:
CoD = BVTo-Be - BV As-Is (d x CoDday) - CDI / CDI
Cost of Doing Nothing (CoDN):
This is the loss per day for not implementing the Solution. Similarly, for d days:
CoDN = BVAs-Is - (d x CoDNday) - CDI / CDI
This Return On Investment (ROI) Modelling must also be set in the context Current State ('As Is') versus Future State ('To Be'). This is where the quantification of the value of AI and a simplified technology underpinning, it leads to creating a compelling argument for your timely Digital Innovations.
With a clear understanding of the ROI Model, it is important to understand how we work with you to map these calculations to the true cost of AI. This is the detailed design, development and delivery costs that determine each phase of your AI-Powered Digital Transformation.
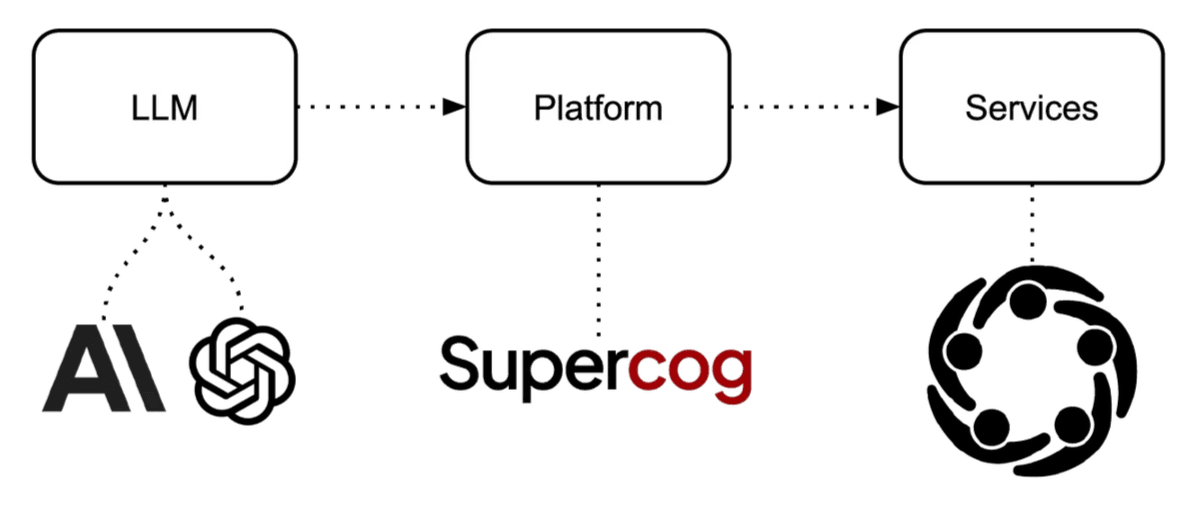
Our AI Pricing Model comprises: Large Language Model (LLM); Platform; and, Services:
1. Large Language Model (LLM)
The choice of LLM to power the Supercog AI Agent Platform will depend on the use case detail and the extent to which Usage Pricing applies, or not. At Being Guided we work closely with Supercog in to determine if the LLM will require Usage Pricing. In the case of simple augmentation solutions, the LLM costs may be amortised into the Supercog Platform costs.
2. Platform
The Supercog Platform Enterprise Pricing Model is crafted through the Value Engineering element of AI Discovery. This may take several different forms of licensing: ranging from a Per User Per Month Recurring Subscription Fees to clearly-defined Usage Pricing. Whatever the outcome, the Platform pricing will be clear, related directly to the Value Engineering and ROI Model generated.
3. Services
The Professional Services element of our AI Pricing Model are usually based on Fixed-Price terms but could be a collaborative effort among two or more organisations, including Supercog Services, a system integrator as partner, and/or an internal IT organisation.
This leads on to the third element for delivery: AI Enabling.
AI Enabling
Ai Enabling is a rapidly-evolving features of AI-Powered Digital Transformation. As described above, this is augmentation of human tasks (as a copilot) and/or automation of human tasks.
Design Thinking and Value Engineering provides a solid foundation for AI Discovery and to create proof-of-concepts of autonomous automation versus augmenting human task management. As the underlying Large Language Models (LLMs) improve, so too our AI solutions will generate yet more automation and simplication of IT.
Supercog AI Agent Platform combines unstructured knowledge with structured data, knowledge search and real-time system access. So this could be a 'Text-to-Action' use case combining various IT system records with information extracted from multiple documents.
Supercog AI Agent Platform comprises three elements:
Large Lanuage Model (LLM). This powers the Agent. You can choose amongst many different LLMs, including (but not limited to): GPT4o-mini; and, Claude Sonnet 3.5.
Agent. The Agent Instructions describe the work that you would like the Agent to perform. When you want to devote your Agent to a specific task, then you will want to explain that task in the Instructions.
Tools. You enable agents to perform work by giving them tools. Without any Tools an Agent is limited to the capabilities of the underlying LLM. Tools include: Amazon S3; Discord; DuckDB; GitHub; Gmail; HubSpot; Jira; Salesforce; ServiceNow; Slack; Snowflake; and, Zapier.
References
Stanford d.school. https://dschool.stanford.edu/about
- Lewrick, M. and Hatamleh, O. (2024) AI and Innovation. John Wiley & Sons. https://amzn.to/4dWBWqY
- Liedtka, J., Chen, E., Foley, N. and Kester, D. (2024) Experimentation Field Book. New York: Columbia University Press. https://www.amazon.co.uk/Experimentation-Field-Book-Step-Step/dp/0231214170
